DDPM
Published:
This is the introduction of DDPM.
DDPM
Destroy
\(x=x_0→x_1→x_2→⋯→x_{T−1}→x_T=z\)
$x_t = \alpha_t + \beta_t\epsilon_t$ where $\alpha_t^2 + \beta_t^2 = 1$ and $\beta_t$ is close to 0. This means that $x_t$ was converted to noise little by little.
After we expand $x_t$, we get
\[x_t = \underbrace{(\alpha_t \cdots \alpha_1)}_{\texttt{denote as }\bar{\alpha}_t} x_0 + \underbrace{\sqrt{1 - (\alpha_t \cdots \alpha_1)^2}}_{\texttt{denote as }\bar{\beta}_t} \bar{\varepsilon}_t, \quad \bar{\varepsilon}_t \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I)\]Select proper $\bar{\alpha}_t \approx 0$ because the $x_t$ was mostly replaced by the noise after t steps.
Reconstruct
\[L = ‖x_{t-1} - μ(x_t)‖^2\]Since $x_{t-1} = \frac{1}{\alpha_t}(x_t - \beta_t\varepsilon_t)$ from previous part,we can design $μ(x_t)$ as following:
\[μ(x_t) = \frac{1}{\alpha_t}(x_t - \beta_t\varepsilon_θ(x_t, t)), \text{ where θ is parameter.}\] \[\implies‖x_{t-1} - μ(x_t)‖^2 = \frac{\beta_t^2}{\alpha_t^2}‖\varepsilon_t - \varepsilon_θ(x_t, t)‖^2\]Then we will neglect $\frac{\beta_t^2}{\alpha_t^2}$ and expand $x_t$:
\[x_t = \alpha_tx_{t-1} + \beta_t\varepsilon_t = \alpha_t(\bar{\alpha}_{t-1} x_0 + \bar{\beta}_{t-1}\bar{\varepsilon}_{t-1}) + \beta_t\varepsilon_t \\ = \bar{\alpha}_t x_0 + \alpha_t\bar{\beta}_{t-1}\bar{\varepsilon}_{t-1} + \beta_t\varepsilon_t\] \[\implies L = ‖\varepsilon_t - \varepsilon_θ(\bar{\alpha}_t x_0 + \alpha_t\bar{\beta}_{t-1}\bar{\varepsilon}_{t-1} + \beta_t\varepsilon_t, t)‖^2\]Modification
Since we need to sample 4 paramter, $x_0, t, \varepsilon_t, \bar{\varepsilon}_{t-1}$, the training is not stable.
Since $\varepsilon_t, \bar{\varepsilon}_{t-1}$ are indepedant and both normal distribution, we can do some replacement and simplify the loss to:
\[‖\varepsilon - \frac{\bar{\beta_t}}{\beta_t}\varepsilon_θ(\bar{\alpha}_{t} x_0 + \bar{\beta_t}\varepsilon, t)‖^2, \quad \varepsilon \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I)\]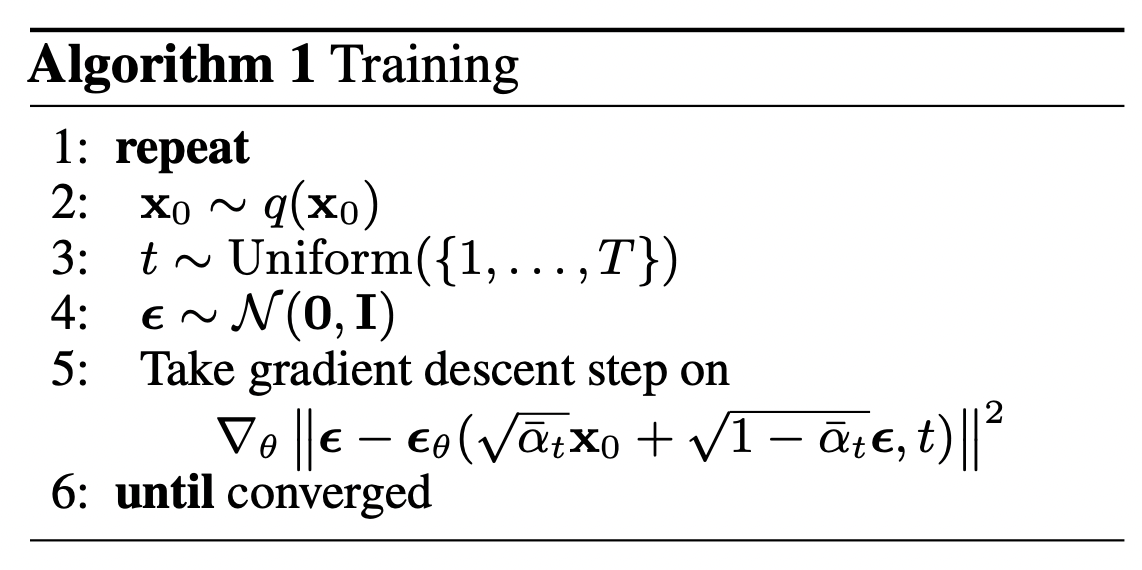
Sampling
After training ,we can randomly sample $x_T \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I)$ and do generation based on $x_{t-1} = \frac{1}{\alpha_t}(x_t - \beta_t\varepsilon_θ(x_t, t)) \quad$
This is similar to the autoregressive decoding with Greedy Search. If you want to do Random Sample, add noise term is required. This is because in the training part, we use $x_t$ to predict $x_{t-1}$ and $x_t$ has some random noise, we will add some random noise when generation.
\[x_{t-1} = \frac{1}{\alpha_t}(x_t - \beta_t\varepsilon_θ(x_t, t)) + \sigma_t z, \quad z \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I) \quad\]We usuallly set $σ_t = \beta_t$, which means that dstroy and reconstruction have the same varience.

